| References: |
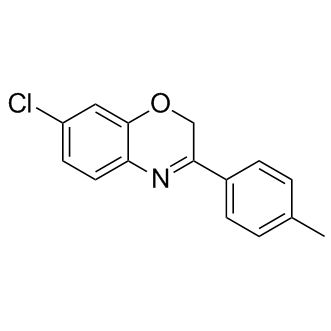
AR7 is a retinoic acid receptor α (RARα) antagonist.
InVitro: Chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA) contributes to cellular quality control and the cellular response to stress through the selective degradation of cytosolic proteins in lysosomes. Decrease in CMA activity occurs in aging and in age-related disorders. Signaling through the retinoic acid receptor alpha (RARα) inhibits CMA. AR7, an RARα antagonist, significantly activates CMA activity in mouse fibroblasts. A marked increase in CMA-activating potency is found when AR7 and GR1 are combined, supporting their cooperative effect. Treatment with the transcriptional repressor Actinomycin D partially reduces the stimulatory effect of AR7 on CMA, consistent with transcriptional changes contributing to the upregulation of CMA. The antagonistic effect of the retinoid derivatives likely results from a combination of tight binding to RARα and high stability. For AR7, the bulky aromatic rings offer excellent interaction contacts with the surrounding hydrophobic RARα residues such as Met406, Leu266, Leu398 and Ile270. |