| References: |
Gambogic Acid activates caspases with EC50 of 0.78-1.64 μM and competitively inhibits Bcl-XL, Bcl-2, Bcl-W, Bcl-B, Bfl-1 and Mcl-1 with IC50 of 1.47, 1.21, 2.02, 0.66, 1.06 and 0.79 μM, respectively.
IC50 Value: 1.21 uM (Bcl-2); 1.47 uM (Bcl-xl)
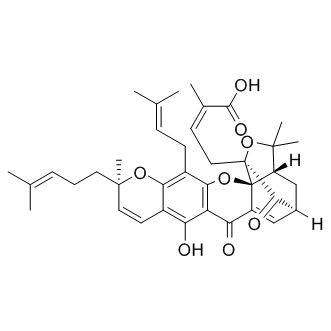
in vitro: Gambogic acid is a xanthonoid that is derived from the brownish or orange resin from Garcinia hanburyi. This natural chemical has shown promising antitumor activity in clinical trials with mice. Gambogic Acid activates caspases with EC50 of 0.78-1.64 μM and competitively inhibits Bcl-xl, Bcl-2, Bcl-w, Bcl-B, Bfl-1 and Mcl-1 with IC50 of 1.47 μM, 1.21 μM, 2.02 μM, 0.66 μM, 1.06 μM and 0.79 μM, respectively. Gambogic Acid significantly inhibited the growth of JeKo-1 cells in a dose- and time-dependent manner. The maximum GA-induced cytotoxity was evident at 36 hrs exposure to 4 μg/mL GA. The IC50 of 12, 24 and 36 hrs of GA treatment for JeKo-1 cells was 0.73, 0.72 and 0.55 μg/mL respectively. GA induces apoptosis in JeKo-1 cells but not in normal bone marrow cells, which was involved in reducing the membrane potential of mitochondria, activating caspases-3, -8 and -9 and decreasing the ratio of Bcl-2 and Bax without cell cycle arresting . GA potentially enhanced level of PHD2, the most important HIF hydroxylase, and showed no effect on PHD1 and PHD3. Transient transfection of siRNA of PHD2 could eliminate GA-induced VEGF secretion increase.
in vivo: GA showed a higher absorption rate than other intestinal segments (P < 0.05) and kept unchanged in duodenum after addition in drug concentration in rats . GBA significantly inhibited the LPS-induced release of pro-inflammatory factors both in cell lines and mice serum, thereby protecting mice from endotoxin shock. |