| References: |
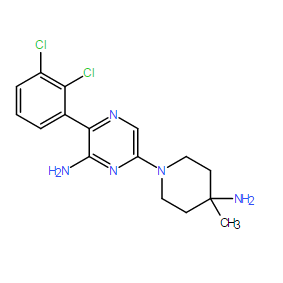
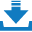
SHP099 is a potent, selective, orally bioavailable, and efficacious SHP2 inhibitor with IC50 =0.07 μM and p-ERK modulation in cells IC50 = 0.250 μM. SHP099 exhibits dose-dependent pathway inhibition and antitumor activity in xenograft models. SHP-099 stabilizes SHP2 in an auto-inhibited conformation, concurrently binds to the interface of the N-terminal SH2, C-terminal SH2, and protein tyrosine phosphatase domains, thus inhibiting SHP2 activity through an allosteric mechanism. SHP099 suppresses RAS–ERK signaling to inhibit the proliferation of receptor-tyrosine-kinase-driven human cancer cells in vitro and is efficacious in mouse tumor xenograft models. SHP099’s activity provides evidence that pharmacological inhibition of SHP2 is a viable strategy to target RTK-driven cancers and presents a new chemical tool for further interrogation of the multifaceted cellular functions of SHP2 in development, tumorigenesis, RTK-driven drug resistance and immune-checkpoint modulation.SHP2 is a nonreceptor protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP) encoded by the PTPN11 gene involved in cell growth and differentiation via the MAPK signaling pathway. SHP2 also purportedly plays an important role in the programmed cell death pathway (PD-1/PD-L1). Because it is an oncoprotein associated with multiple cancer-related diseases, as well as a potential immunomodulator, controlling SHP2 activity is of significant therapeutic interest. |