| References: |
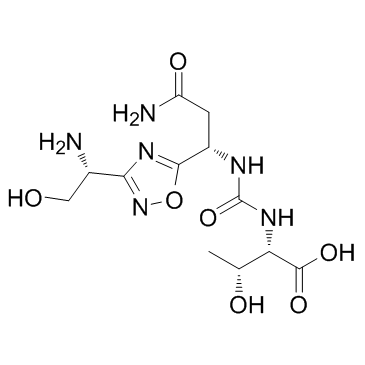
CA-170 is an orally bioavailable small molecule inhibitor of the immune checkpoint regulatory proteins programmed cell death ligand-1 (PD-L1; B7-H1; CD274), PD-L2, and V-domain immunoglobulin (Ig) suppressor of T-cell activation (VISTA; programmed death 1 homolog; PD1H; PD-1H), with potential negative immune checkpoint regulatory and antineoplastic activities. CA-170 targets and binds to PD-L1, PD-L2 and VISTA. This inhibits PD-L1/PD-L2/VISTA-mediated signaling, abrogates the PD-L1-, PD-L2- and VISTA-induced suppression of T-lymphocyte immune responses, enhances cytotoxic T-cell proliferation and activation against tumor cells, increases cytokine production by T-cells, and inhibits tumor cell growth. PD-L1, PD-L2 and VISTA, negative checkpoint molecules of immune activation, play key roles in the suppression of T-cell functions.Pre-clinically, CA-170 inhibition of PD-L1 or VISTA-mediated suppression of T cell function was tested in vitro using human, monkey, or mouse cells. In vivo anti-tumor activity was examined in multiple syngeneic mouse models. Pts with advanced solid tumors or lymphomas, age ≥ 18, ECOG ≤1 and adequate organ function are treated with escalating doses of oral CA-170 daily during Ph 1a. Ph 1b dose expansion will enrich enrollment for selected pt population possibly responsive to this novel inhibitor. Primary objectives: safety, maximum tolerated dose and recommended Phase 2 dose. Secondary objectives: pharmacokinetics and anti-tumor activity. Exploratory endpoints: biomarkers and pharmacodynamic (PD) effects in periphery and tumor tissues.CA-170 rescues in vitro T cell effector function with activity comparable to that of PD-1 or VISTA blocking antibodies. Oral CA-170 inhibits the growth of mouse syngeneic tumors (B16 melanoma, CT26 and MC38 colon carcinoma), enhances peripheral T cell activation, and promotes the activation of tumor infiltrating CD8+ T cells in vivo. In humans, a total of 19 patients have been treated across 6 dose levels (50 - 800 mg). No dose limiting toxicity has been observed. CA-170 exhibits generally dose proportional plasma exposure with T1/2 of ∼ 4-9.5 hours. Evidence of peripheral T cell activation was observed with an increased proportion of circulating CD8+ and CD4+ T cells expressing activation markers, CD69 and CD134, following oral dosing. |