| References: |
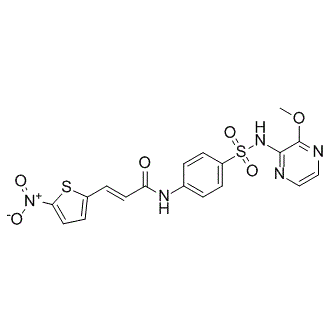
Necrosulfonamide (NSA) is a very specific and potent necrosis inhibitor with an IC50 less than 0.2 uM. It specifically blocks necrosis downstream of receptor-interacting serine-threonine kinase 3 (RIP3) activation. RIP3 is a key signaling molecule in the programmed necrosis pathway. Treating cells with NSA arrested necrosis at a specific step at which RIP3 formed discrete punctae in cells. Different from Necrostatin-1, NSA does not inhibit the necrosis-induced RIP1 and RIP3 interactions. NSA targets MLKL, a critical substrate of RIP3 during induction of necrosis. It binds the N-terminal of MLKL, covalently modifies Cys86 of human MLKL, and prevents necrosome from interacting with its downstream effectors. |